Unlocking the Mysteries of the Mind Through Quantitative EEG Brain Mapping Techniques in Mental Wellness Evaluation
Unlocking the Mysteries of the Mind Through Quantitative EEG Brain Mapping Techniques in Mental Wellness Evaluation
Blog Article
Understanding the individual mind is a complex endeavor, particularly when it pertains to psychological health. Conventional methods of assessment often rely on interviews and surveys, which can occasionally overlook important details about how the mind functions. This is where qEEG brainwave analysis, or qEEG, enters into play. qEEG is a specialized technique that assesses neural signals in the brain. By analyzing these brainwaves, psychological health experts can obtain important insights into a person's mental state, aiding to enhance diagnosis and intervention.
qEEG functions by applying small electrodes on the scalp to record brain signals. These sensors measure electrical signals produced by nerve cells, the units in the cerebrum that communicate with each other. The information gathered is then processed and displayed as a set of patterns. Each type of brainwave—such as α, beta, delta, and θ—relates to different mental conditions and functions. For example, alpha oscillations are often associated with calmness, while β waves are linked to active cognition and issue resolution. By examining these patterns, healthcare providers can detect abnormalities that may suggest psychological health issues.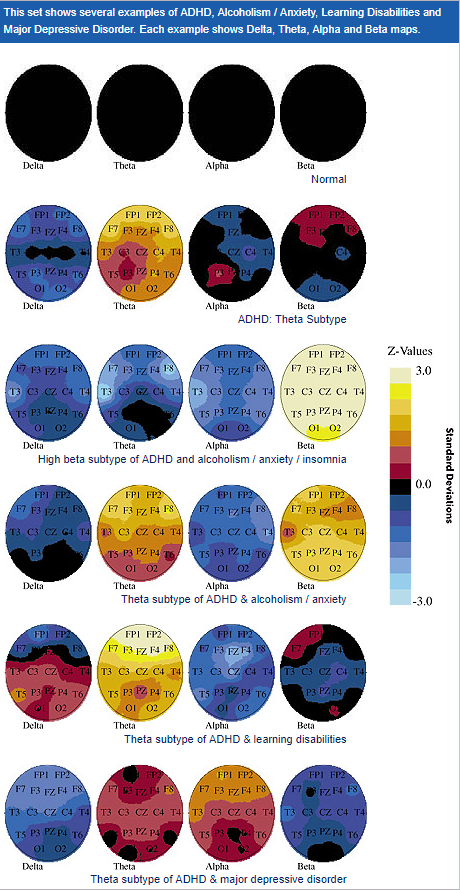
One of the significant benefits of qEEG is its capability to provide objective data. In contrast to conventional evaluations that rely on subjective reports from patients, qEEG provides a distinct view of neural activity. This clarity can help reduce biases in assessment and result to more precise intervention plans. For instance, if a patient is experiencing anxiety, qEEG can show particular patterns of brain activity that are associated with stress conditions. This data enables psychological health professionals to tailor interventions more effectively, whether through therapy, pharmaceuticals, or other treatments.
Moreover, qEEG can be especially beneficial in tracking intervention progress. By conducting qEEG assessments at different points during therapy, healthcare providers can monitor changes in neural function over period. This continuous assessment helps determine whether a treatment is effective or if adjustments are needed. For example, if a patient is not responding to a particular medication, qEEG may show that their neural activity has not changed in a way that indicates improvement. This feedback loop can lead to more personalized and effective mental health care.
In conclusion, qEEG brain mapping is a powerful tool in the field of mental health assessment. By providing objective data about brain activity, it enhances the understanding of various mental health conditions. This technique not only aids in accurate diagnosis but also helps in tracking intervention success. As psychological health experts persist to explore the potential of qEEG, it holds promise for improving the lives of individuals facing mental qEEG brain mapping for neurofeedback applications health challenges. With continuous investigation and progress in techniques, the secrets of the brain may turn more apparent, leading to better outcomes for those in need of support.